The escalating threat of climate change is dramatically reshaping the landscape of homeownership, particularly in vulnerable regions like Southern California. Wildfires, floods, extreme heat, and deteriorating air quality are no longer abstract future risks, but tangible present dangers impacting property values, insurance affordability, and even the very decision of where to buy a home. This shift is evident in the growing awareness among homebuyers, with over 80% now factoring climate risks into their purchasing decisions. Zillow’s data paints a stark picture, revealing a significant increase in climate risk for newly listed homes since 2019, with the majority facing major risks from extreme heat and wind exposure. Furthermore, substantial percentages are at risk from wildfires, flooding, and poor air quality, especially in densely populated western regions. This data underscores the urgent need for comprehensive strategies to mitigate these risks and adapt to a changing climate.
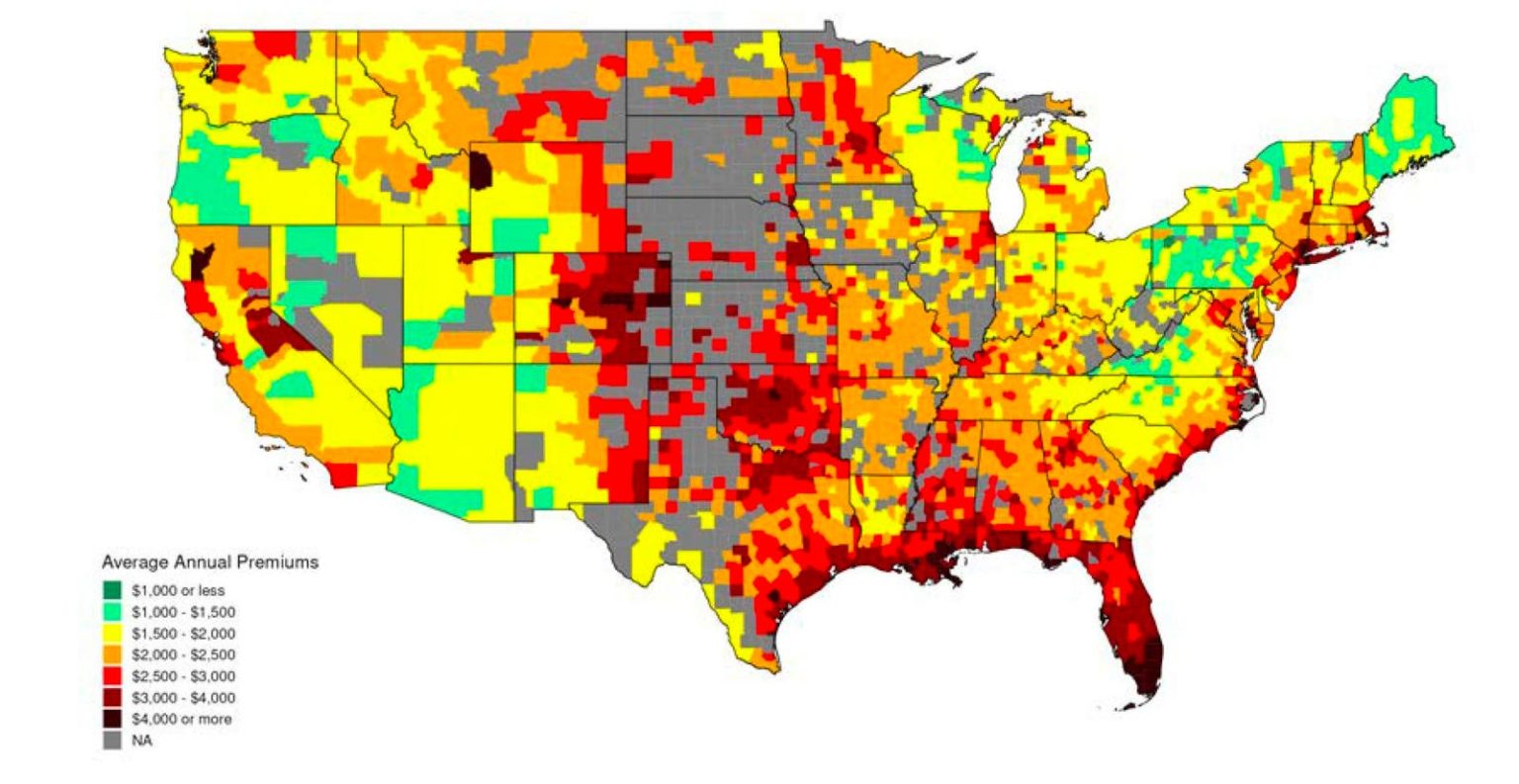
The increasing prevalence of climate-related risks is directly impacting the affordability and availability of home insurance. As insurers grapple with the rising costs of payouts from frequent and severe natural disasters, premiums are skyrocketing, placing an additional burden on homeowners and potential buyers. This financial strain, coupled with the existing housing affordability crisis, can make homeownership unattainable for many, further exacerbating existing inequalities. Beyond individual homeowners, these rising insurance costs have broader economic repercussions. Depressed property values, reduced investment in vulnerable areas, and strained state budgets for disaster relief contribute to a vicious cycle of financial instability. The interconnectedness of these factors necessitates a multifaceted approach involving policymakers, insurers, homeowners, and the real estate industry to address the complex challenges posed by climate change.
The severity and frequency of climate-related disasters are rapidly outpacing both policy responses and infrastructure resilience. Experts warn that the current framework for dealing with these events is inadequate for the challenges ahead. The increasing number of climate-related disasters annually underscores the urgent need for more proactive and comprehensive strategies. While investments in climate tech solutions offer a glimmer of hope, the recent decline in funding reflects a concerning trend. Simultaneously, the economic fallout from these events, including declining stock prices for utilities and insurance companies, and strained state resources, further complicates the situation. This dynamic highlights the urgent need for both immediate and long-term solutions that address not only the immediate aftermath of disasters but also the underlying vulnerabilities that exacerbate their impact.
The escalating costs of home insurance are not merely a localized problem but a systemic risk to the housing market and the broader financial system. The parallels drawn with the 2008 crisis underscore the potential for a cascading effect if insurance costs continue to rise unchecked. As property values decline and affordability shrinks, the stability of mortgage markets is threatened. The urgency of this situation demands a collaborative effort among stakeholders, including regulators, homeowners, and the insurance industry, to develop comprehensive solutions. Accurate risk assessment, transparent pricing, and responsible lending practices are essential components of a stable and resilient housing market in the face of climate change.
Addressing the complex challenges of climate risk and insurance affordability requires a systems-level approach. Regulators face the difficult task of balancing the need for accurate risk pricing with the desire to keep insurance rates affordable, while homeowners must play a role in understanding risk factors and adapting their decisions accordingly. Transparency in risk assessment is paramount, enabling informed decision-making for both buyers and sellers. Tools like Zillow, which already provide some climate risk data, can further enhance transparency by incorporating insurance rate information into property listings. This integration would empower potential buyers to fully understand the financial implications of purchasing a home in a high-risk area, fostering greater responsibility and enabling informed decision making.
Technological advancements, especially in the realm of artificial intelligence, offer promising avenues for improving the efficiency and effectiveness of insurance practices. AI-powered tools can streamline claims processing, enhance risk assessment, and provide more accurate and personalized insurance policies. By leveraging visual data and sensor inputs, insurance companies can expedite damage assessment and accelerate the claims process, reducing financial strain on homeowners after a disaster. The ability of AI to analyze complex systems and model future events also holds immense potential for more accurately predicting and managing climate-related risks, paving the way for a more resilient and sustainable insurance landscape. The development and implementation of these technologies are crucial for adapting to the evolving challenges of climate change and ensuring the long-term stability of the housing market.