Verizon Communications’ stock price dipped to $38.44, pushing its dividend yield above 7% based on its annualized $2.71 dividend. This enticing yield prompts a closer examination of the role and significance of dividends in investment returns, particularly in light of the historical performance of the broader market. The example of the S&P 500 ETF (SPY) over the period from 1999 to 2012 highlights this importance. While the share price itself declined slightly during this time, the accumulated dividends contributed significantly to the overall positive return, demonstrating how dividends can cushion against price depreciation and even generate positive returns in otherwise flat or negative markets. Comparing this historical average annual return of around 1.6% (even with reinvestment) to Verizon’s potential 7% yield underscores the apparent attractiveness of such a high yield, provided it is sustainable. Furthermore, Verizon’s inclusion in the S&P 500 Index signifies its standing as a large-cap company, adding another layer of consideration for potential investors.
The S&P 500 example serves as a powerful illustration of the long-term impact of dividends. While capital appreciation is often the primary focus for investors, consistent dividend payments can significantly enhance overall returns, especially during periods of market stagnation or decline. The $25.98 in dividends received per share of SPY over the thirteen-year period significantly outweighed the $4.67 decline in share price, transforming a potential loss into a respectable gain. This underscores the importance of a holistic view of investment returns, considering both price fluctuations and the compounding power of reinvested dividends. A high dividend yield, like the 7% offered by Verizon, can be a compelling factor for income-seeking investors, particularly in comparison to the historical returns of the broader market.
However, the sustainability of a high dividend yield is a critical factor to consider. Dividend payouts are not guaranteed and are often influenced by a company’s financial performance and profitability. Therefore, simply chasing high yields without considering the underlying financial health of the company can be a risky strategy. Analyzing Verizon’s historical dividend payments and its overall financial performance is essential to assess the likelihood of the current dividend being maintained or potentially even increased in the future. Investors need to evaluate whether the company’s earnings can consistently support the dividend payout, and whether the company has a history of prioritizing dividend payments to its shareholders.
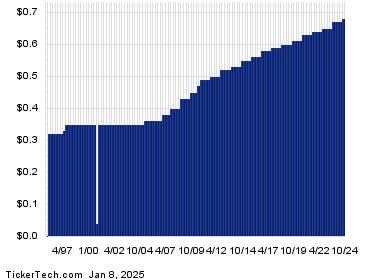
This brings us to the core of evaluating the attractiveness of Verizon’s 7% yield: determining its sustainability. Examining the company’s historical dividend chart can provide valuable insights into its dividend policy and the consistency of its payouts. A long history of steadily increasing or maintaining dividends suggests a commitment to returning value to shareholders and may indicate a higher likelihood of the current dividend being sustainable. Conversely, a history of erratic dividend payments or dividend cuts can be a warning sign, indicating potential financial instability or changing priorities within the company. Therefore, a thorough analysis of Verizon’s dividend history is crucial before relying on the 7% yield as a primary investment thesis.
Beyond the dividend yield, a comprehensive investment analysis should consider other factors such as Verizon’s competitive landscape, its growth prospects, and its overall financial health. The telecommunications industry is constantly evolving, facing technological disruptions and intense competition. Understanding Verizon’s position within this dynamic landscape is essential to assessing the long-term viability of its business model and its ability to generate the earnings needed to support its dividend. Analyzing factors such as revenue growth, profitability margins, and debt levels can provide a more complete picture of the company’s financial strength and its ability to sustain its dividend payments in the long run.
In conclusion, while Verizon’s 7% dividend yield is undeniably attractive, investors should exercise caution and conduct thorough due diligence before making any investment decisions. The S&P 500 example demonstrates the long-term benefits of dividend income, but it also highlights the importance of considering total returns, not just yield. The sustainability of Verizon’s dividend is paramount, and a careful examination of its historical dividend payments, financial performance, and competitive positioning is essential to evaluate the true attractiveness of this investment opportunity. Ultimately, a well-informed investment decision should be based on a holistic assessment of the company’s financial health, its growth prospects, and the likelihood of the 7% yield being maintained over the long term.