The allure of high dividend yields is undeniable, especially in uncertain market conditions. Western Union (WU), a member of the Russell 3000 index, briefly saw its stock price dip to $10.39, pushing its annualized dividend yield above the impressive 9% mark based on its $0.94 annual dividend. This scenario highlights the crucial role dividends play in total investment returns. Historically, dividends have contributed significantly to the overall performance of the stock market, often offsetting price declines or even generating positive returns in otherwise stagnant periods. The importance of this income stream cannot be overstated, as demonstrated by the example of the iShares Russell 3000 ETF (IWV). Over a 12-year period, the ETF’s price experienced a marginal decline. However, the accumulated dividends over the same period transformed a nominal loss into a substantial double-digit gain, underscoring the power of consistent dividend payments in long-term investment strategies. While a 1.0% annualized total return even with reinvested dividends might appear modest, the prospect of a sustainable 9% yield offered by Western Union presents a compelling investment thesis, prompting a closer examination of its dividend payout sustainability.
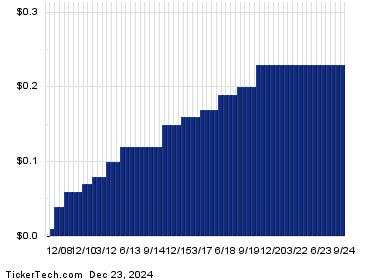
The comparison between a low total return from a broad market index and a potentially high yield from a single stock emphasizes the critical need to assess the reliability of dividend payments. Dividend amounts are inherently variable, mirroring the fluctuations in a company’s profitability. While the high yield of Western Union is enticing, investors must scrutinize the company’s dividend history to determine its consistency and ability to maintain such payouts. Past dividend trends provide valuable insights into the company’s financial health and dividend policy, serving as a gauge for future distributions. A thorough analysis of WU’s dividend history chart is indispensable for evaluating the sustainability of its current yield and forming realistic expectations regarding future income streams. Simply relying on the current yield without understanding the underlying factors that drive it can lead to misleading conclusions and potentially disappointing investment outcomes.
Furthermore, evaluating dividend sustainability requires a broader understanding of the company’s financial performance beyond its historical dividend payments. Factors such as revenue growth, earnings stability, debt levels, and industry dynamics play crucial roles in influencing a company’s capacity to distribute dividends consistently. A company facing declining revenues, increasing debt, or operating in a highly competitive and volatile industry might struggle to maintain its dividend payout, even if its historical record appears strong. Therefore, a comprehensive assessment of Western Union’s financial health and its competitive landscape is essential to gauge the long-term viability of its dividend policy.
The example of the iShares Russell 3000 ETF returns illustrates a crucial principle: while capital appreciation can be elusive, especially in volatile market conditions, dividends provide a stable and predictable source of income that can significantly enhance total returns over the long term. This highlights the potential benefits of incorporating dividend-paying stocks into a diversified portfolio, particularly for investors seeking regular income or aiming to mitigate the impact of market fluctuations. However, the attraction of high dividend yields should not overshadow the importance of careful due diligence. Chasing yield without considering the underlying fundamentals can lead to investing in companies with unsustainable payout ratios, putting both principal and income at risk.
The article’s focus on Western Union’s high dividend yield serves as a springboard for a broader discussion about the role of dividends in investment strategies. While high yields can be attractive, they must be evaluated in the context of the company’s overall financial health and the sustainability of its dividend policy. A rigorous analysis of historical dividend payments, combined with a thorough assessment of the company’s financial strength and industry position, is paramount for making informed investment decisions. The allure of a 9% yield, or any high yield for that matter, should not overshadow the importance of a comprehensive understanding of the company’s ability to maintain such payouts in the future.
Finally, comparing Western Union’s potential 9% yield to the long-term returns of a broad market index, such as the Russell 3000, provides valuable context for evaluating its attractiveness. While the Russell 3000 delivered a modest total return over the period cited, including reinvested dividends, it represents a diversified portfolio of 3000 companies, mitigating the risks associated with investing in a single stock. Western Union’s potentially higher yield represents a concentrated bet on the company’s performance and its ability to maintain its dividend payouts. This higher potential return comes with higher risk, underscoring the importance of careful analysis and prudent decision-making. Investors should consider their risk tolerance, investment goals, and the overall market environment before making investment decisions based on dividend yields alone.