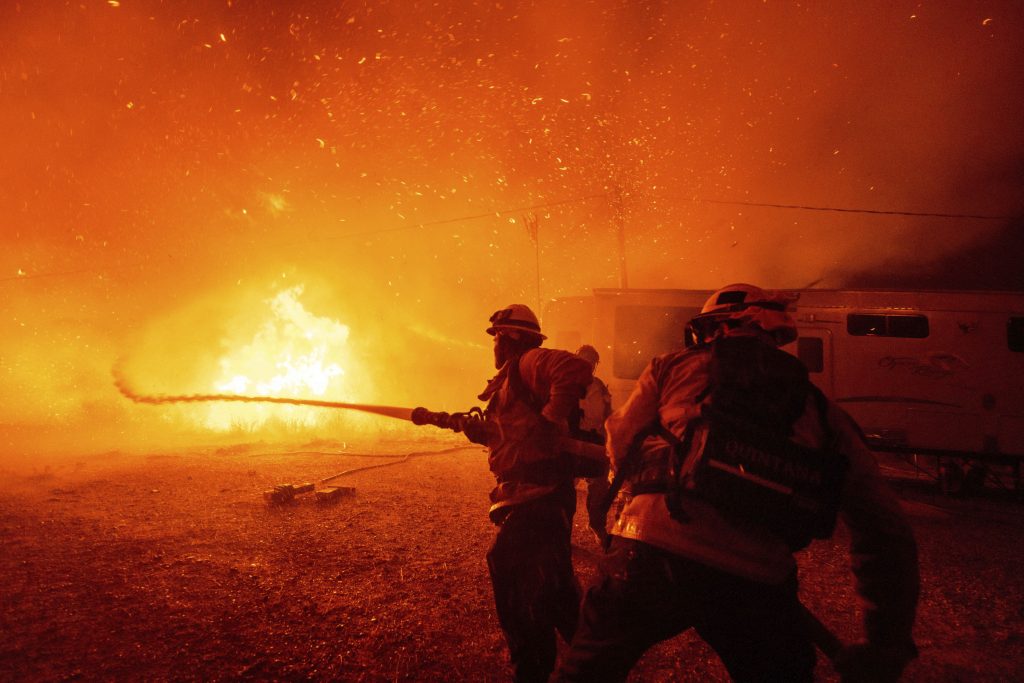
The wildfire crisis in California continues to unfold, with nine active blazes scorching the landscape as of Friday morning. These fires have tragically claimed the lives of 28 people and displaced thousands from their homes, leaving a trail of devastation across the state. The situation remains critical, particularly in Los Angeles County, where several fires pose ongoing threats to communities. The confluence of dry vegetation, strong winds, and low humidity has created a volatile environment, making fire suppression efforts challenging. Adding to the urgency, new fires erupted on Thursday, rapidly consuming hundreds of acres and prompting evacuations.
Red flag warnings, indicative of extreme fire danger, remain in effect across much of Southern California. Strong Santa Ana winds, gusting up to 55 mph, continue to fuel the flames and hamper containment efforts. Firefighters are battling these blazes on multiple fronts, working tirelessly to protect lives and property. Despite the challenging conditions, they have made significant progress in containing some of the larger fires, offering a glimmer of hope amid the destruction. However, the persistent threat of new ignitions and the rapid spread potential under the prevailing weather conditions necessitate continued vigilance and preparedness.
The Fig Fire, which ignited Thursday evening in Riverside County, prompted initial evacuations but has since been largely contained, with its forward progress halted. Similarly, the Sepulveda Fire in Los Angeles County has been brought under control, and evacuation orders have been lifted. However, other fires continue to rage. The Border 2 Fire, burning near the U.S.-Mexico border in San Diego County, has grown to 600 acres and remains uncontained, posing a threat to critical communication infrastructure. While no homes are currently threatened, the fire’s location in rugged terrain presents challenges for firefighters.
The Hughes Fire, which exploded to over 10,000 acres, remains a major concern. While containment efforts have reached 36%, approximately 31,000 people remain under mandatory evacuation orders, with another 23,000 under evacuation warnings. The combination of high winds and dry conditions has contributed to the fire’s rapid growth and intensity. The Palisades Fire, while 75% contained, has already left a devastating mark, destroying over 6,800 structures and claiming 11 lives. A curfew remains in effect in the mandatory evacuation areas as firefighters continue their efforts to fully contain the blaze.
The Eaton Fire, the second-largest active fire, stands at 95% containment after burning over 14,000 acres and claiming 17 lives. While the fire’s progression has slowed, the extensive damage underscores the destructive power of these wildfires. The Clay Fire in Riverside County, although smaller in scale, is 85% contained. The Laguna Fire in Ventura County, while 70% contained, still poses a potential threat, with evacuation warnings remaining in place. The Gibbel Fire, also in Riverside County, is 60% contained after burning 20 acres.
The National Weather Service continues to emphasize the critical fire weather conditions, warning that any new ignition has the potential to rapidly escalate into a major fire. The combination of dry fuels, strong winds, and low humidity creates an environment ripe for combustion. Residents in high-risk areas are urged to have evacuation plans in place and remain vigilant. The upcoming weekend may bring some relief, with a cold front expected to bring at least light rain to some areas. However, until the weather conditions significantly improve, the threat of wildfires will persist.
The ongoing wildfire crisis in California serves as a stark reminder of the increasing frequency and intensity of extreme weather events. The convergence of climate change, drought conditions, and overgrown vegetation has created a tinderbox scenario, making communities increasingly vulnerable to these devastating blazes. The human cost, in terms of lives lost, homes destroyed, and communities disrupted, is immense. As these fires continue to burn, the focus remains on protecting lives, containing the flames, and supporting those affected by this ongoing disaster. The long-term recovery process will be extensive, requiring significant resources and community support. Beyond the immediate response, addressing the underlying factors that contribute to wildfire risk, such as forest management and climate change mitigation, will be crucial in preventing future tragedies of this scale.
The repeated cycles of wildfires in California highlight the need for comprehensive approaches to wildfire management and community resilience. This includes implementing effective forest management practices, such as prescribed burns and fuel reduction efforts, to minimize the risk of large-scale fires. Investing in fire-resistant building materials and implementing stricter building codes in high-risk areas can also help protect homes and communities. Improving early warning systems and evacuation procedures is critical to ensuring timely and effective responses to wildfire threats.
Furthermore, addressing the root causes of climate change, such as reducing greenhouse gas emissions, is essential for mitigating the long-term risks of extreme weather events, including wildfires. The increasing frequency and intensity of droughts and heat waves, exacerbated by climate change, create ideal conditions for wildfires to ignite and spread rapidly. Investing in renewable energy sources, promoting energy efficiency, and transitioning to a low-carbon economy are crucial steps in mitigating climate change and reducing wildfire risk.
Public awareness and education campaigns can play a vital role in promoting fire safety and preparedness. Educating communities about wildfire risks, encouraging the creation of defensible space around homes, and promoting responsible behavior in fire-prone areas can help reduce the likelihood of human-caused ignitions and minimize the impact of wildfires. Community-based wildfire protection programs can empower residents to take an active role in protecting their homes and neighborhoods.
The ongoing wildfire crisis in California underscores the importance of collaboration and coordination among various stakeholders, including government agencies, fire departments, community organizations, and residents. Sharing information, coordinating resources, and implementing collaborative strategies are crucial for effectively responding to wildfires and mitigating their impacts.
Finally, supporting the mental and emotional well-being of those affected by wildfires is essential. The trauma of losing homes, livelihoods, and loved ones can have long-lasting effects. Providing access to mental health services, counseling, and community support networks can help individuals and communities cope with the emotional aftermath of these devastating events. The long road to recovery from the California wildfires requires a collective effort to rebuild communities, restore ecosystems, and enhance resilience in the face of future challenges.