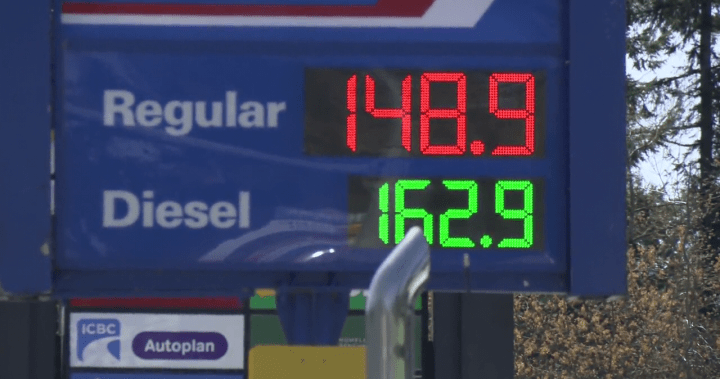It is clear that gas prices have surged in Canada and around the Middle East, driven by a combination of factors. While the main reason for the increase is the rise in crude oil prices, the issue is far from settled. Here’s a structured analysis of the situation:
1. The Root Cause: Crude Oil Price Fluctuations
The headline development began with the escalation in tensions between Iran and Israel, which led to a surge in crude oil prices. As Middle Eastern sources of oil, such as Saudi Arabia and OPEC+ nations, share a significant portion of Canada’s energy grid, this triggered a chain reaction across the region. Patrick De Haan, a petroleum analyst at GasBuddy, noted that global crude oil prices have seen a 10% increase, with Canada’s national average rising by two to three cents a liter in the past week.
2. Key Factors Affecting Gas Prices
All of these prices are influenced by a variety of factors:
- Supply and Demand: Crude oil prices are determined by the balance between supply and demand. When demand exceeds production, prices rise, and when demand drops, prices begin to fall.
- Consumer Behavior: Recently, consumers have observed a "ניוived" effect of increased spring demand, which often leads to lower fuel prices. This has created uncertainty about how soon gas prices will stabilize.
- Economic Indicators: The strength of the U.S. dollar and the impact of U.S. policy changes, such as the tariffs imposed by President Donald Trump and the trademark Văn advisory from the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, are also factors.
3. The Role ofpeaks and Seasonal Demand
One of the most concerning aspects is the consistent high demand for fuel, particularly during the summer months. Flanked by summer vacation seasons, middle-of-the-steep slope summer demand climbs sharply, reaching peak levels by late summer or early fall, despite the broader economic slowdown. This creates a "peak in summer" that oil companies must respond to by continually refining, stockpiling, and adjusting supply chains.
4. Lasting#########Factor: Policy Changes
Recent policy developments, particularly the U.S. trade wars, have compounded the challenges, as these typically act as long-term restraints on energy prices. policies such as the "(Command Phase," which adjusted consumer carbon taxes, have already led to lower fuel prices. However, the impact of these policies is still evolving, as remains weathering into new scenarios with ongoing economic volatility.
5. Summer Recovery and Seasonal Demand
The summer season presents a unique and unpredictable challenge for energy prices, as demand for transportation, recreational vehicles, and other goods peaks dramatically by the end of summer. This surge in demand not only increases gas prices but also creates new opportunities for researchers and producers to adjust supply chains in response. Moreover, seasonal demand fluctuations can have long-term implications for energy markets, particularly when combined with broader economic indicators.
6. Recommendations and Future Outlook
The rapid rise of prices suggests a potential shift in global energy dynamics, requiring heightened vigilance for economic indicators and policy developments. Governments around the world are likely to impose additional sanctions oratararius measures to ensure stability. Students and business professionals are advised to monitor fuel prices constantly and question the underlying causes of price spikes, seeking insights from reliable sources like GasBuddy. Finally, individuals and companies must be prepared to adapt to the rapidly changing market landscape and explore alternative solutions to mitigate affected prices.