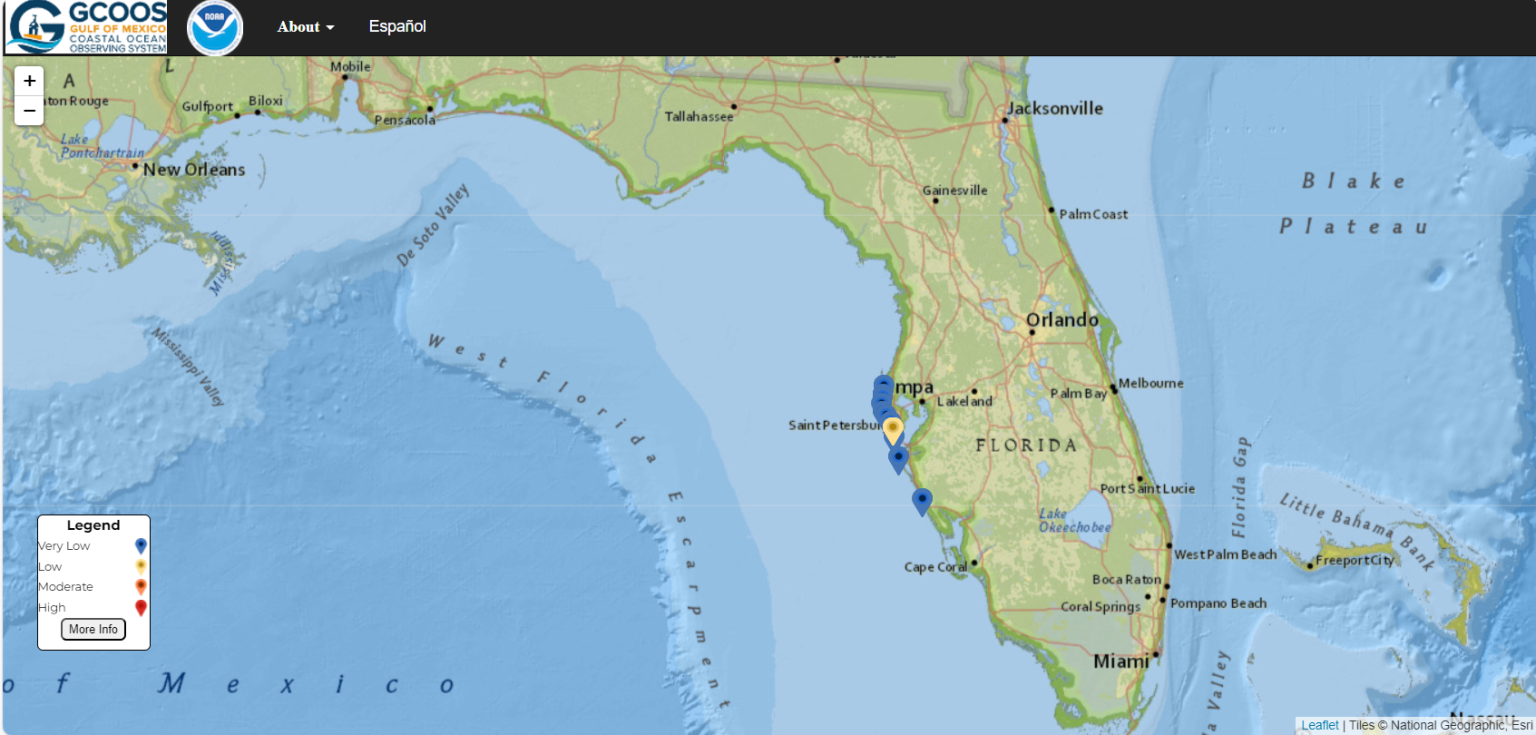
Floridians residing along the Gulf Coast, particularly in the Tampa Bay area, are currently experiencing a "high risk" of respiratory irritation due to red tide, as announced by the National Weather Service (NWS). The warning, disseminated through their social media channels, indicates that the risk extends to various beaches in Pinellas County for the next 36 hours. The affected regions stretch from Clearwater Beach to the south of Venice, emphasizing significant health concerns for locals and visitors to these popular coastal areas. The situation stems from harmful algal blooms (HABs) caused by the harmful algae known as Karenia brevis, which has been cited as a primary factor for adverse health effects on humans, marine life, and the broader ecosystem.
Red tide, a phenomenon related to the proliferation of algae, can produce potent toxins that lead to serious health risks. According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), such outbreaks can result in debilitating or even fatal human illnesses, although these instances are relatively rare. The NOAA describes the conditions leading to red tide: when algae colonies grow uncontrollably, they can create hazardous effects for individuals enjoying beach activities, as well as local fish, shellfish, marine mammals, and bird populations. The NWS shared that respiratory issues are often exacerbated when onshore winds occur, especially during this time of year when fluctuating weather fronts pass through, causing a buildup in concentrated algae along the coast.
Richard Stumpf, a NOAA oceanographer, elaborated on the nature of these red tide events, noting their prevalence particularly in late fall. The occurrence of respiratory irritation warnings is not atypical during these blooms, primarily resulting from shifts in wind patterns. Stumpf pointed out that while today’s winds are onshore, a forecasted change to offshore winds might help reduce irritants at the beaches tomorrow. The variability of red tide also means that not all areas will experience significant problems, indicating that conditions are highly localized and dependent on environmental factors like wind direction and concentration of the algae in specific locales.
In light of the ongoing red tide situation, the NWS has emphasized the importance of monitoring real-time conditions at the individual beaches through an interactive map provided by the Gulf of Mexico Coastal Ocean Observing System. This access could prove essential for residents and visitors looking to minimize exposure to harmful irritants. Alongside these concerns about air quality and health, southeastern Florida is also facing weather challenges as a cold front swept through the region over the recent weekend. This has resulted in temperatures plummeting below freezing in certain areas, prompting additional weather warnings and concerns about public safety.
The NWS in Tallahassee has cautioned that the arrival of the dry cold front signals a sustained period of frigid temperatures, with overnight lows forecasted to remain cold for several mornings. The warnings indicate potential risks to vegetation and agriculture, as frost conditions may endanger sensitive crops. Particularly vulnerable populations—such as young children, the elderly, and the homeless—are urged to take extra precautions during this cold spell to ensure their safety and wellbeing. Authorities emphasize the need for protective measures against the adverse weather conditions, highlighting the interconnected challenges posed by both the red tide and the cold front on the lives of Floridians.
As Florida navigates through these challenges, the combination of health risks from red tide and the dangers posed by colder temperatures illustrates the complex environmental situation facing coastal communities. With significant effects on air quality, marine ecosystems, and public safety, ongoing communication from agencies like the NWS and NOAA is crucial in helping residents manage these risks. As the NWS suggests, checking conditions frequently will be key for individuals looking to engage in outdoor activities in affected areas. Adapting to such rapidly changing environments requires diligence and awareness from both citizens and local authorities.