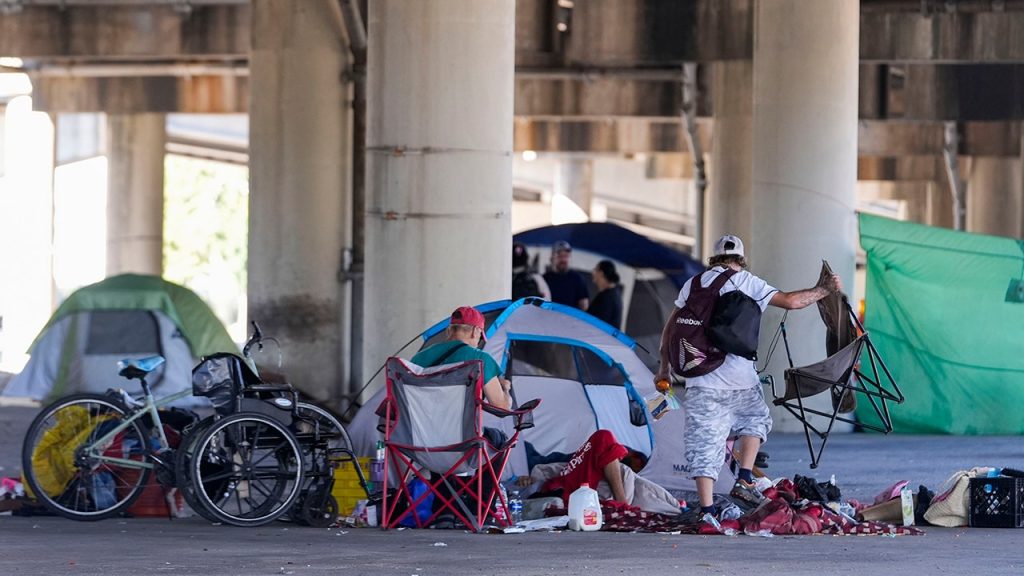
The 2024 Annual Homelessness Assessment Report, released by the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD), paints a concerning picture of homelessness in the United States. The report, which represents a point-in-time count from January 2024, documented over 770,000 people experiencing homelessness on a single night, a stark 18% increase compared to 2023. This surge is attributed to a confluence of factors, including a rise in asylum seekers, a persistent lack of affordable housing, and the devastating impact of natural disasters like the Maui wildfires. The report acknowledges that the data, collected a year prior, may not fully reflect current conditions given policy changes and evolving circumstances, specifically citing the Biden administration’s subsequent actions to address border security and irregular migration.
One of the most significant findings of the report is the disproportionate impact on families experiencing homelessness. This population saw a staggering 39% increase nationwide. The report highlights the role of migration in this surge, noting that in communities reporting significant influxes of asylum seekers, family homelessness more than doubled. This contrasts sharply with other communities, where the increase was less than 8%. While the report acknowledges the impact of rising rents, it also notes that rental costs had begun to stabilize and even decline in some cities by the time of publication, following significant increases in the wake of the pandemic and years of insufficient housing construction.
The report underscores the complex interplay of factors contributing to the rise in homelessness. While the influx of asylum seekers exerted considerable pressure on certain communities, particularly impacting families, the underlying issue of affordable housing availability remained a significant challenge. The pandemic exacerbated this pre-existing crisis, contributing to escalating rental costs. Furthermore, natural disasters, especially the Maui wildfires, displaced thousands, forcing many into emergency shelters and contributing to the overall increase in homelessness recorded in the point-in-time count.
Despite the overall increase in homelessness, the report highlights a significant success story: a substantial reduction in veteran homelessness. The number of homeless veterans reached its lowest recorded level, decreasing by nearly 8% compared to 2023. This positive trend is attributed to targeted interventions and programs like the HUD-VASH program, which provides rental assistance and supportive services to veterans. The success in reducing veteran homelessness demonstrates the effectiveness of focused strategies and underscores the potential for similar approaches to address homelessness in other populations.
In response to the report’s findings and recognizing the evolving landscape of homelessness, the Biden-Harris administration announced a series of measures aimed at tackling the crisis. These include expanding partnerships with the Department of Health and Human Services to enhance support services and allocating nearly $40 million in funding specifically for veteran homelessness programs. These initiatives build on existing efforts and reflect the administration’s commitment to addressing the root causes of homelessness and ensuring access to safe and affordable housing for all Americans.
The 2024 HUD report serves as a critical reminder of the persistent challenges surrounding homelessness in the United States. While the report captures a snapshot in time, it underscores the need for comprehensive and sustained efforts to address the complex factors driving homelessness. The significant increase in overall homelessness, particularly among families, highlights the urgent need for solutions that address both immediate needs and underlying systemic issues. The success in reducing veteran homelessness, however, provides a glimmer of hope and demonstrates the potential for targeted interventions to make a significant difference. Moving forward, a multi-faceted approach that encompasses increased access to affordable housing, targeted support services for vulnerable populations, and effective disaster response strategies will be crucial in combating this complex and persistent societal challenge.