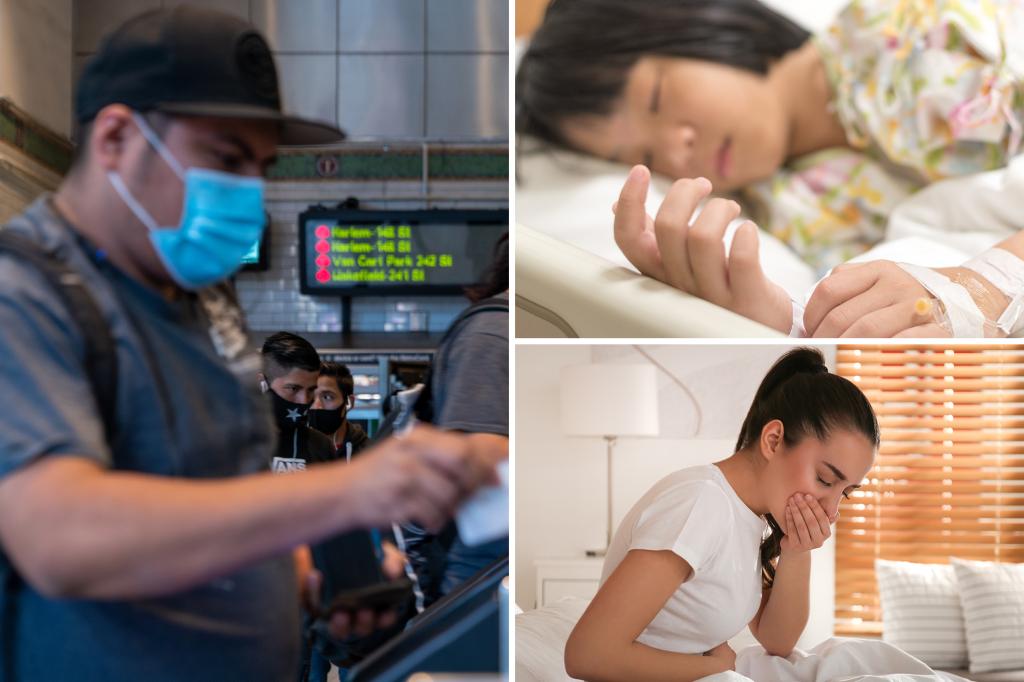
The city of New York is experiencing a significant surge in viral illnesses, particularly norovirus and influenza, posing a public health concern for residents. Norovirus infections saw a dramatic 159% increase in December 2024 compared to the same period in 2023, with reported cases jumping from 488 to 1,264. This upward trend continued into the new year, with a 30% increase in norovirus cases in the first two weeks of 2025 compared to the same period in the previous year. Health officials acknowledge that the actual number of norovirus cases is likely much higher due to underreporting, as not everyone seeks medical attention and testing for the illness. Norovirus, often referred to as the “stomach flu,” typically manifests with symptoms like vomiting and diarrhea, although severe cases can, albeit rarely, lead to fatalities.
Concurrent with the norovirus surge, influenza cases are also on the rise in New York City. Nearly 15,000 individuals tested positive for the flu in the week ending January 11, 2025, representing a 10% increase from the preceding week and a 23% increase compared to the same period in 2024. While the current flu season has witnessed one pediatric death attributed to influenza, this marks a decrease from the three pediatric flu-related deaths recorded by the same time last year. The city health department’s data collection currently does not include tracking adult deaths related to either influenza or norovirus, limiting the comprehensive understanding of the overall impact of these illnesses on the adult population.
The concurrent outbreaks of norovirus and influenza underscore the importance of preventative measures to curb the spread of these highly contagious illnesses. Health experts emphasize the critical role of hand hygiene, particularly thorough and frequent handwashing, as a primary defense against both viruses. Individuals experiencing symptoms consistent with either norovirus or influenza are strongly advised to remain at home to prevent further transmission. This includes avoiding public spaces, workplaces, and social gatherings until symptoms subside. Early detection through testing can also contribute to containing the spread, allowing individuals to take appropriate precautions and seek necessary medical care.
The substantial increase in norovirus infections warrants heightened public awareness and proactive measures to mitigate its impact. The reported 159% surge in cases within a single month indicates a rapid spread within the community, raising concerns about potential strain on healthcare resources. The virus’s ability to cause significant gastrointestinal distress, coupled with its high transmissibility, necessitates a collective effort to minimize its spread. The fact that the reported cases likely represent an underestimation of the true prevalence further emphasizes the need for heightened vigilance and adherence to preventative measures.
The escalating influenza cases present a parallel challenge, demanding continued efforts to encourage vaccination and promote responsible health practices. While the decrease in pediatric deaths compared to the previous year offers a glimmer of positive news, the overall increase in flu cases emphasizes the ongoing need for preventative measures. The substantial 23% rise in influenza infections compared to the previous year underscores the dynamic nature of viral transmission and the importance of adapting public health strategies accordingly. Encouraging flu vaccination remains a crucial strategy for reducing the severity and spread of the illness.
The convergence of these two viral outbreaks underscores the vulnerability of urban populations to rapidly spreading illnesses and highlights the necessity for a multi-pronged public health approach. This includes enhancing public awareness campaigns regarding preventative measures, ensuring readily available testing resources, and promoting timely access to appropriate medical care. The city’s current limitation in tracking adult deaths associated with these illnesses represents a gap in data collection that could hinder a comprehensive understanding of the full impact of these outbreaks. Strengthening surveillance and data collection efforts could provide valuable insights for developing and refining public health strategies in the future. The combined effect of these viral outbreaks presents a significant challenge to public health, demanding a proactive and comprehensive response to protect the well-being of the community.