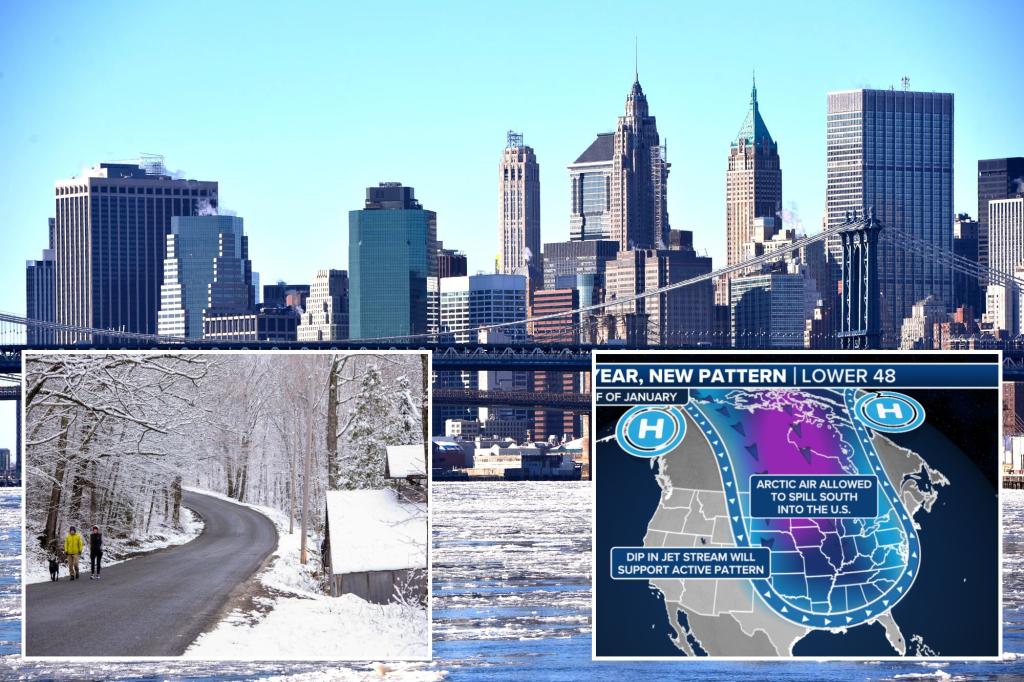
The eastern half of the United States is bracing for a potentially historic cold snap in January, with meteorologists predicting the coldest temperatures in a decade. This frigid forecast stems from a southward dip of the polar vortex, a swirling mass of cold air normally confined to the Arctic. While December saw a mix of cold spells and unusual warmth, averaging out to near-normal temperatures overall, the impending January freeze is expected to be far more extreme and persistent. Experts warn of temperatures plummeting 20 degrees below average in some regions, with wind chills in the Midwest potentially dropping below zero. Even traditionally warmer areas like the Gulf Coast and Florida could experience freezing conditions, though precise temperature predictions remain challenging at this stage. This dramatic shift in weather patterns follows a December that, despite starting cold, concluded with unusually warm conditions across much of the nation, particularly in the West where temperatures soared up to 13 degrees above normal.
The anticipated cold wave, expected to commence around Thursday, will initially manifest across the Rocky Mountains and gradually spread eastward. The most severe temperature drop is projected to occur within the next one to two weeks, plunging the affected regions into a deep freeze. The intensity and duration of this cold spell are attributed to the southward migration of the polar vortex, a phenomenon that occurs when the air currents normally containing the arctic air weaken. This weakening allows the frigid air to escape its usual confines and spill southward, displacing the polar vortex and bringing arctic conditions to lower latitudes. The strength of the current forecast lies in the unusual consensus among various weather models, all pointing towards the arrival of this intense cold air mass. This high level of confidence distinguishes this forecast from more typical polar vortex predictions, which often carry significant uncertainty.
The southward shift of the polar vortex not only unleashes arctic air but also sets the stage for potentially disruptive winter storms. The interaction between the frigid air mass, altered pressure systems, and the movement of the polar vortex creates conditions conducive to significant snowfall and icy precipitation. Meteorologists warn of a “pretty good chance” of these storms developing during the middle to end of next week, potentially impacting the Southeast with snow or ice. While the precise track and intensity of these storms remain uncertain at this time, the potential for widespread winter weather disruptions is a significant concern. This cold is anticipated to persist throughout January, offering little respite until February arrives.
The weakening of the polar vortex, allowing the escape of Arctic air, is a recurring meteorological phenomenon, albeit with varying intensity and duration. The stability of the vortex is crucial for maintaining the typical distribution of global temperatures. When the vortex weakens, the contained Arctic air spills southward, displacing the vortex and bringing frigid conditions to lower latitudes. This southward movement is often accompanied by high winds and volatile weather patterns, as the displaced cold air interacts with warmer air masses. The current forecast suggests a significant weakening of the polar vortex, leading to a prolonged period of exceptionally cold temperatures across the eastern United States.
The expected January freeze serves as a stark reminder of the 2014 polar vortex event, which brought similarly harsh conditions and resulted in tragic consequences. Over 20 fatalities were attributed to the extreme cold across the country, as even regions unaccustomed to severe winter weather, such as Georgia, experienced temperatures plummeting below 10 degrees Fahrenheit. The 2014 event highlighted the vulnerability of populations to extreme cold, particularly in areas where infrastructure and preparedness may be less geared towards such conditions. The current forecast raises concerns about potential impacts on vulnerable populations, infrastructure, and daily life, emphasizing the need for preparedness and preventative measures.
As January approaches, residents in the eastern half of the United States are advised to prepare for a prolonged period of exceptionally cold weather. The southward plunge of the polar vortex brings with it not only frigid temperatures but also the potential for significant winter storms. Ensuring adequate heating, protecting exposed pipes, and stocking up on essential supplies are crucial steps in mitigating the risks associated with this extreme cold snap. Staying informed about weather updates and heeding advisories from local authorities will be essential for navigating this challenging period. The severity of the forecast warrants a proactive approach to preparedness, minimizing potential disruptions and ensuring safety throughout the duration of the cold wave.